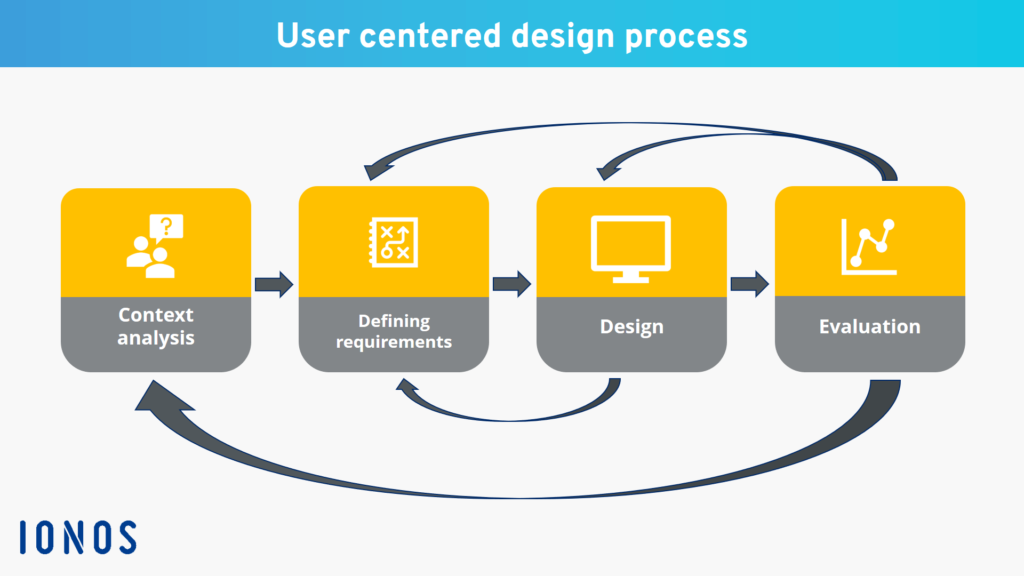
In today’s highly competitive market, creating products that truly resonate with users is a key factor in achieving success. One of the most effective approaches to ensuring a product’s success is through User-Centered Design (UCD). UCD is a design philosophy and process that prioritizes the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users at every stage of product development. By focusing on the end user, companies can craft products that are not only functional but also intuitive, engaging, and satisfying to use.
What is User-Centered Design?
User-Centered Design is a design methodology that aims to create products by deeply understanding the target users. It involves iterative testing and feedback, ensuring that users’ needs are consistently met throughout the product development lifecycle. UCD emphasizes that the users are not just passive recipients of a product, but active participants whose feedback shapes the design and functionality.
The UCD process typically involves five stages: research, design, prototyping, testing, and implementation. Each stage is centered around understanding user needs and iterating based on insights gathered from real users. This makes UCD fundamentally different from traditional design approaches, which may prioritize technical specifications, cost constraints, or brand guidelines over user experience.
Why User-Centered Design Matters
- Improved User Satisfaction One of the primary benefits of UCD is the creation of products that users find easy to use and enjoyable. When a product is designed with the user’s needs and pain points in mind, it’s more likely to solve real problems. Whether it’s a mobile app, a website, or a physical product, the goal is to reduce frustration, confusion, and errors, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
For instance, consider the difference between two online shopping experiences. One site may have a cluttered layout, confusing navigation, and hidden checkout options, while another might have a clean design, intuitive flow, and easy-to-find buttons. The latter’s user-centric design leads to a smoother, more enjoyable shopping experience, which in turn increases the likelihood of repeat customers and positive reviews.
- Increased Accessibility User-Centered Design places a strong emphasis on accessibility, ensuring that products are usable by as many people as possible, including those with disabilities. Accessibility can include designing for people with visual, auditory, or motor impairments, as well as ensuring the product functions well on various devices and screen sizes.
For example, a well-designed mobile app may include features like high contrast modes, screen reader support, and voice navigation to accommodate users with different needs. By integrating accessibility into the design from the outset, companies can create products that cater to a wider audience, fostering inclusivity.
- Enhanced Usability Usability refers to how easily a user can accomplish their goals using a product. A product that is intuitive and simple to navigate reduces the learning curve and increases user engagement. Through UCD, designers can focus on creating seamless interactions, avoiding unnecessary complexity, and improving the overall user journey.
A great example of this is the evolution of smartphones. Early models had complex menus and unintuitive controls, while modern smartphones like the iPhone have simple touch interfaces, easily understandable icons, and gesture-based navigation. This simplicity is the result of years of user feedback and iterative design—hallmarks of User-Centered Design.
- Higher Conversion Rates and Customer Retention In the world of digital products, user experience directly impacts business outcomes like conversion rates and customer retention. A product that is easy to use and meets the user’s needs is more likely to engage users and encourage them to complete desired actions—whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a service, or returning to the product in the future.
For instance, a website optimized through UCD principles may see higher conversion rates by streamlining the checkout process, ensuring fast load times, and providing clear instructions. This not only helps users but also boosts the bottom line. Similarly, apps that are designed to be user-friendly see better retention rates, as users are more likely to continue using a product they find simple and enjoyable.
- Reduced Development Costs and Risks At first glance, incorporating user feedback and iterative testing might seem like a time-consuming and expensive process. However, UCD can actually reduce long-term development costs by identifying issues early in the process before they become more costly to fix. Prototypes, user testing, and feedback loops help designers pinpoint usability flaws, technical limitations, and unclear requirements early on.
Additionally, by developing products that better meet the needs of users, companies reduce the risk of product failure. A product that is aligned with user expectations and desires is more likely to succeed in the market, leading to reduced waste in terms of both time and resources.
- Building Trust and Brand Loyalty User-Centered Design fosters trust because it shows users that their needs and feedback are valued. When a product consistently performs as expected, is easy to navigate, and meets its intended purpose, it builds credibility and encourages loyalty. Users are more likely to return to a product that they trust, and they are more likely to recommend it to others.
Conclusion
Incorporating User-Centered Design into the development process leads to products that are not only functional but also enjoyable and efficient for the user. By understanding users’ behaviors, pain points, and needs, companies can create products that stand out in a crowded market, foster trust and loyalty, and ultimately drive business success. In an era where user experience is paramount, adopting UCD is not just a smart choice—it’s essential for building products that make a lasting impact.